On keyboards
17th April 2009There cannot be too many Linux users who go out and partner a Microsoft keyboard with their system but my recent cable-induced mishap has resulted in exactly that outcome. Keyboards are such standard items that it is not so possible to generate any excitement about them, apart from RSI-related concerns. While I wasn’t about to go for something cheap and nasty that would do me an injury, going for something too elaborate wasn’t part of the plan either, even if examples of that ilk from Microsoft and Logitech were sorely tempting.
Shopping in a bricks and mortar store like I was has its pluses and its minuses. The main plus points are that you see and feel what you are buying with the main drawback being that the selection on offer isn’t likely to be as extensive as you’d find on the web, even if I was in a superstore. Despite the latter, there was still a good deal available. There were PS/2 keyboards for anyone needing them but USB ones seemed to be the main offer with wireless examples showcased too. Strangely, the latter were only available as kits with mice included, further adding to the cost of an already none too cheap item. The result was that I wasn’t lured away from the wired option.
I didn’t emerge with what would have been my first choice because that was out of stock but that’s not to say that what I have doesn’t do the job for me. Key action is soft and cushioned rather than clicky like that to which I am accustomed; some keyboards feel like they belong on a laptop but not this one. There are other bells and whistles too with a surprising number of them working. The calculator and email buttons number among these along with the play/pause, back and forward ones for a media player; I am not so convinced about the volume controls though an on-screen indicator does pop up. You’d expect a Microsoft item to be more Windows specific than others but mine works as well as anything else in the Ubuntu world and I have no reason to suspect that other Linux distros would spurn it either. Keyboards are one of those “buy-it-and-forget-it” items and the new arrival should be no different.
Blogging with Word 2007
1st February 2007It seems strange to say it but I am making good use of Word’s blogging capabilities. Having had WordPress.com’s blog editor mangle one of my posts – incidentally while using Opera as my browser -- is the cause of this turn of events.
When setting up new accounts, there are a number of presets available to be used to work with major blogging providers such as Blogger, WordPress, and TypePad. This is not all though as it is possible to hook up to other blogs in a more generic fashion. In fact, I have able to hook up to my other WordPress-powered blog; hosted on the same server as my personal website and with all of the associated programming and scripting handled by myself. Where you have a number of accounts set up in the application, a drop-down menu appears in the post so that you can select the account to be used.
Speaking of drop down menus embedded in the post, you can add categories to a post from the blog server’s own collection and you can have more than one in any post. This feature is a boon as is the ability to edit posts that are already on there but Word only seems to show a subset of all the posts on the server, about 20 I think, rather than every single one. Another caveat is that you need to use a separate window for each post or you’ll end up overwriting posts in error. Whether this is a result of RSS feed settings or is intrinsic to Word itself remains something that I have yet to discern. As it is Word, formatting, insertion of objects such as hyperlinks and images is very much part of the package. That said, uploading images via this route was not something that I tested until I was writing this post but it seems to work well.
Apart from the irritations discussed above, I did find Word crashing a few times but no data were lost thanks to its seemingly excellent file recovery capabilities, a definite counterpoint to some of my experiences with Word’s file recovery feature in previous versions. Eventually, the Office Diagnostics tools kicked in to see if all was well and, after carrying out both hardware (memory, hard drive, etc.) and software checks, an installation repair was performed. Let’s see if this resolves the issue. Even so, the crash repair and diagnostics were not something that I had seen to the same extent in previous versions of Office and they did look pretty impressive.
In summary, Word does seem to be good blogging tool but I wouldn’t use it on its own because of its inability to download a full list of posts for editing. A blog’s own interface will remain necessary for that. Also, Word is far from being the only “offline” blog editor out there and I am tempted to take a look at the likes of BlogJet and w.bloggar.
Forcing Ubuntu (and Debian) to upgrade to a newer distribution version
8th October 2008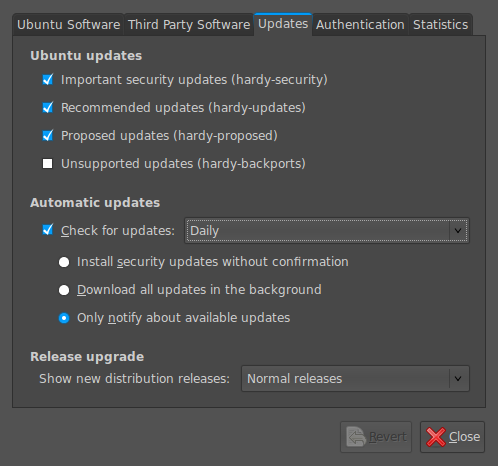
Ubuntu is usually good at highlighting the existence of a new version of the distribution through its Update Manager. That means that 8.10 should be made available to you at the end of the month so long as you have sorted the relevant setting for 8.04 to realise what has happened. That lives in System > Administration > Software Sources > Updates. If you haven’t done that, then 8.04 will continue regardless since it is a long term supported release.
Otherwise, it’s over to the command line to sort you out. One of the ones below will do with the first just carrying out a check for a new stable version of Ubuntu and the second going all the way:
sudo update-manager -c
sudo update-manager -p
if you are feeling more adventurous, you can always try the development version and this checks for one of those (I successfully used this to try out the beta release of Intrepid Ibex from within a Wubi instance on my laptop):
sudo update-manager -d
Neither of the above are available on Debian so they seem to be Ubuntu enhancements. That is not to say that you cannot force the issue with Debian; it’s just that the more generic variant is used and, unless, you have gone fiddling with visudo, you will need to run this as root (it works in Ubuntu too):
update-manager --dist-upgrade
Compressing a VirtualBox VDI file for a Linux guest
6th June 2016In a previous posting, I talked about compressing a virtual hard disk for a Windows guest system running in VirtualBox on a Linux system. Since then, I have needed to do the same for a Linux guest following some housekeeping. The Linux distribution used is Debian so the instructions are relevant to that and maybe its derivatives such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint and their kind.
While there are other alternatives like dd, I am going to stick with a utility named zerofree to overwrite the newly freed up disk space with zeroes to aid compression later on in the process for this and the first step is to install it using the following command:
apt-get install zerofree
Once that has been completed, the next step is to unmount the relevant disk partition. Luckily for me, what I needed to compress was an area that I reserved for synchronisation with Dropbox. If it was the root area where the operating system files are kept, a live distro would be needed instead. In any event, the required command takes the following form with the mount point being whatever it is on your system (/home, for instance):
sudo umount [mount point]
With the disk partition unmounted, zerofree can be run by issuing a command that looks like this:
zerofree -v /dev/sdxN
Above, the -v switch tells zerofree to display its progress and a continually updating percentage count tells you how it is going. The /dev/sdxN piece is generic with the x corresponding to the letter assigned to the disk on which the partition resides (a, b, c or whatever) and the N is the partition number (1, 2, 3 or whatever; before GPT, the maximum was 4). Putting all this together, we get an example like /dev/sdb2.
Once, that had completed, the next step is to shut down the VM and execute a command like the following on the host Linux system ([file location/file name] needs to be replaced with whatever applies on your system):
VBoxManage modifyhd [file location/file name].vdi --compact
With the zero filling in place, there was a lot of space released when I tried this. While it would be nice for dynamic virtual disks to reduce in size automatically, I accept that there may be data integrity risks with those so the manual process will suffice for now. It has not been needed that often anyway.
Performing parallel processing in Perl scripting with the Parallel::ForkManager module
30th September 2019In a previous post, I described how to add Perl modules in Linux Mint while mentioning that I hoped to add another that discusses the use of the Parallel::ForkManager module. This is that second post and I am going to keep things as simple and generic as they can be. There are other articles like one on the Perl Maven website that go into more detail.
The first thing to do is ensure that the Parallel::ForkManager module is called by your script and having the following line near the top will do just that. Without this step, the script will not be able to find the required module by itself and errors will be generated.
use Parallel::ForkManager;
Then, the maximum number of threads needs to be specified. While that can be achieved using a simple variable declaration, the following line reads this from the command used to invoke the script. It even tells a forgetful user what they need to do in its own terse manner. Here $0 is the name of the script and N is the number of threads. Not all these threads will get used and processing capacity will limit how many actually are in use so there is less chance of overwhelming a CPU.
my $forks = shift or die "Usage: $0 N\n";
Once the maximum number of available threads is known, the next step is to instantiate the Parallel::ForkManager object as follows to use these child processes:
my $pm = Parallel::ForkManager->new($forks);
With the Parallel::ForkManager object available, it is now possible to use it as part of a loop. A foreach loop works well though only a single array can be used with hashes being needed when other collections need interrogation. Two extra statements are needed with one to start a child process and another to end it.
foreach $t (@array) {
my $pid = $pm->start and next;
<< Other code to be processed >>
$pm->finish;
}
Since there often is other processing performed by script and it is possible to have multiple threaded loops in one, there needs to be a way of getting the parent process to wait until all the child processes have completed before moving from one step to another in the main script and that is what the following statement does. In short, it adds more control.
$pm->wait_all_children;
To close, there needs to be a comment on the advantages of parallel processing. Modern multi-core processors often get used in single threaded operations and that leaves most of the capacity unused. Utilising this extra power then shortens processing times markedly. To give you an idea of what can be achieved, I had a single script taking around 2.5 minutes to complete in single threaded mode while setting the maximum number of threads to 24 reduced this to just over half a minute while taking up 80% of the processing capacity. This was with an AMD Ryzen 7 2700X CPU with eight cores and a maximum of 16 processor threads. Surprisingly, using 16 as the maximum thread number only used half the processor capacity so it seems to be a matter of performing one’s own measurements when making these decisions.
Pondering storage options
1st June 2011The combination of curiosity and a little spare time had me browsing online computing technology stores recently. A spot of CD and DVD burning brought on by a flurry of Linux distribution testing reminded me of the possibility. Because I have built up a sizeable library of digital photos, ensuring that I have backups of them is something that needs doing. A 2 GB Samsung external hard drive is brought to life every now and again for that purpose but the prospect of using Blu-Ray discs has appealed to me. After all capacities of 25 GB for single layer discs and 50 GB for dual layer ones sound not inappropriate for my purposes. However, they aren’t a cheap option at the time of writing with each disc costing in the region of £3-4 at one place where I was looking. The cost of BD writers themselves seems not to be so bad though with a few in the £60-100 bracket; any lower than this and you could end up with a combo drive that reads Blu-Ray discs and writes to DVD’s and CD’s so a modicum of concentration is needed. As attractive as the idea might be, the cost of BD media means that I’ll wait a little while before deciding to take the plunge. The price premium at the moment is a reminder of the way that things used to be when CD and DVD writers first came on the market. It is very telling when discs come packaged in jewel cases, something that you won’t see too often with CD’s or DVD’s.
Another piece of storage excitement that hasn’t escaped me is the advent of SSD hard drives. With no moving parts like in conventional hard drives, they bring a speed boost. Concerns about their lifetimes and the numbers of read/write events per drive would stall me when it comes to storing personal data on them but using them for the likes of operating system files sounds attractive, especially with my partiality to Linux perhaps not hammering drives so much. As with any new technology, there is a price premium though a drive big enough for hosting an operating system can be acquired for less than £100. As with many of my hardware purchase brainwaves, there’s no rush but this is an option that I’ll keep at the back of my mind.
Another appealing notion is the idea of getting a NAS so that files can be shared between a few computers. While I have seen prices starting at just above £70 for single disk enclosures, these generally are a more expensive option than external drives and that’s before you consider the cost of any hard drives. Nevertheless, the advantages of a unit containing more than a single hard drive while operating as a print server for any compatible printer too. When you get to 4 or 5 hard drive trays, then the cost has mounted but that could be when they pay their way too. What reminded me of these was a bookazine on home networking that I recently found at a branch of WHSmith’s and their attractions are subject to the networking side of things being made to work without a drama. Once that’s out of the way, then their usefulness really does appeal.
Mulling over all these brainwaves is one thing but it doesn’t mean that the purse strings will become too loose in this age of economic constraint. In fact, pondering them may serve to staunch any impulse purchases. Sometimes, a spot of virtual shopping serves to control things rather than losing the run of oneself.
Never undercutting the reseller…
23rd October 2009Quite possibly, THE big technology news of the week has been the launch of Windows 7. Regular readers may be aware that I have been having a play with the beta and release candidate versions of the thing since the start of the year. In summary, I have found to work both well and unobtrusively. There have been some rough edges when access files through VirtualBox’s means of accessing the host file system from a VM but that’s the only perturbation to be reported and, even then, it only seemed to affect my use of Photoshop Elements.
Therefore, I had it in mind to get my hands on a copy of the final release after it came out. Of course, there was the option of pre-ordering but that isn’t for everyone so there are others. A trip down to the local branch of PC World will allow you to satisfy your needs with full, upgrade (if you already have a copy of XP or Vista, it might be worth trying out the Windows Secrets double installation trick to get it loaded on a clean system) and family packs. The last of these is very tempting: three Home Premium licences for around £130. Wandering around to your local PC components emporium is an alternative but you have to remember that OEM versions of the operating system are locked to the first (self-built) system on which they are installed. Apart from that restriction, the good value compared with retail editions makes them worth considering. The last option that I wish to bring to your attention is buying directly from Microsoft themselves. You would think that this may be cheaper than going to a reseller but that’s not the case with the Family Pack costing around £150 in comparison to PC World’s pricing and it doesn’t end there. That they only accept Maestro debit cards along with credit cards from the likes of Visa and Mastercard perhaps is another sign that Microsoft are new to whole idea of selling online. In contrast, Tesco is no stranger to online selling but they have Windows 7 on offer though they aren’t noted for computer sales; PC World may be forgiven for wondering what that means but who would buy an operating system along with their groceries? I suppose that the answer to that would be that people who are accustomed to delivering one’s essentials at a convenient time should be able to do the same with computer goods too. That convenience of timing is another feature of downloading an OS from the web and many a Linux fan should know what that means. Microsoft may have discovered this of late but that’s better than never.
Because of my positive experience with the pre-release variants of Windows 7, I am very tempted to get my hands on the commercial release. Because I have until early next year with the release candidate and XP works sufficiently well (it ultimately has given Vista something of a soaking), I’ll be able to bide my time. When I do make the jump, it’ll probably be Home Premium that I’ll choose because it seems difficult to justify the extra cost of Professional. It was different in the days of XP when its Professional edition did have something to offer technically minded home users like me. With 7, XP Mode might be a draw but with virtualisation packages like VirtualBox available for no cost, it’s hard to justify spending extra. In any case, I have Vista Home Premium loaded on my Toshiba laptop and that seems to work fine, in spite of all the bad press that Vista has gotten for itself.
Resolving Windows Update Error 0x80244019 on Windows 10
21st August 2015In Windows 10, the preferred place to look if you fancy prompting an update of the system is in the Update & Security section of the Settings application. At the top is the Windows Update and the process usually is as simple as pressing the Check for updates button. For most of the time, that has been my experience but it stopped working on my main Windows 10 virtual machine so I needed to resolve the problem.
Initially, going into the Advanced Options section and deselecting the tick box for Give me updates for other Microsoft products when I update Windows helped but it seemed a non-ideal solution so I looked further. It was then that I found that manually resetting a system’s Windows Updates components helped others so I tried that and restarted the system.
The first part of the process was to right-click on the Start Menu button and select the Windows PowerShell (Admin) entry from the menu that appeared. This may be replaced by Command Prompt (Admin) on your system on your machine, but the next steps in the process are the same. In fact, you could include any commands you see below in a script file and execute that if you prefer. Here, I will run through each group in succession.
From either PowerShell or the Command Prompt, you need to stop the Windows Update, Cryptographic, BITS (or Background Intelligent Transfer Service) and MSI Installer services. To accomplish this, execute the following commands at a command prompt:
net stop wuauserv
net stop cryptSvc
net stop bits
net stop msiserver
With the services stopped, it is then possible to rename the SoftwareDistribution and Catroot2 folders so you can refresh everything to remove them. To accomplish this, execute the following pair of commands using either PowerShell or the Command Prompt:
ren C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old
ren C:\Windows\System32\catroot2 Catroot2.old
Once you have the folders renamed, then you can start the Windows Update, Cryptographic, BITS and MSI Installer services by executing the following commands in either PowerShell or the Command Prompt:
net start wuauserv
net start cryptSvc
net start bits
net start msiserver
Once these have completed, you may close the PowerShell or Command Prompt window that you were using and restart the machine. Going into the Update & Security section of the Settings tool afterwards and pressing the Check for updates button now builds new versions of the folders that you renamed and this takes a little while longer than the usual update process. Otherwise, you could let your system rebuild things in its own time. As it happens, I opted for manual intervention and all has worked well since then.
Using the Windows Command Line for Security Administration
24th July 2009While there are point and click tools for the job, being able to set up new user groups, attaching them to folders and assign uses to them using the command line has major advantages when there are a number to be set up and logs of execution can be retained too. In light of this, it seems a shame that terse documentation along with its being hard to rack down answers to any questions using Google, or whatever happens to be your search engine of choice, makes it less easy to discern what commands need to be run. This is where a book would help but the whole experience is in direct contrast to the community of information providers that is the Linux user community, with Ubuntu being a particular shining example. Saying that, the Windows help system is not so bad once you can track down what you need. For instance, knowing that you need commands like CACLS and NET LOCALGROUP, the ones that have been doing the back work for me, it offers useful information quickly enough. To illustrate the usefulness of the aforementioned commands, here are a few scenarios.
Creating a new group:
net localgroup [name of new group] /comment:”[more verbose description of new group]” /add
Add a group to a folder:
cacls [folder address] /t /e /p [name of group]
The /t switch gets cacls to apply changes to the ACL for the specified folder and all its subfolders, recursive action in other words, while the /e specifies ACL editing rather than its replacement and /p induces replacement of permissions for a given user or group. Using :n, :f, :c or :r directly after the name of a specified user or group assigns no, full, change (write) or read access, respectively. Replacing /p with /r revokes access and leaving off the :n/:f/:c/:r will remove the group or user from the folder.
Add a user to a group:
net localgroup [name of group] [user name (with domain name if on a network)] /add
In addition to NET LOCALGROUP, there is also NET GROUP for wider network operations, something that I don’t have cause to do. Casting the thinking net even wider, I suspect that VB scripting and its ability to tweak the Windows Management Interface might offer more functionality than what is above (PowerShell also comes to mind while we are on the subject) but I am sharing what has been helping me and it can be hard to find if you don’t know where to look.
UNIX
21st September 2012The world of open UNIX variants may not be as vibrant as the Linux one, but UNIX predates Linux by decades so it might be put down to its much greater maturity. BSD seems to predominate here, but the reason may be because of Sun keeping a tight hold on Solaris for so long. Now that Oracle has gone and been more restrictive again, it is the breakaway projects to which we have to look for OpenSolaris successors now. However, the partially free availability of Solaris 10 & 11 may draw some away from the open-source community of the alternative.
BSD
In the world of BSD UNIX, it often is difficult to see what is different between the various projects and some are based on technical excellence using the sort of reasoning that would be inaccessible to many computer users. Though many see the operating system as being one for servers alone, there are PC-focussed versions with PC-BSD being the most notable. The existence of those projects is in start contrast to a mantra that keeps BSD for servers and Linux for desktop systems.
This was a fork of FreeBSD and it seems to have been done for very technical reasons, such as handling of cluster computing and larger disc drives. If the reasons make sense to you, then it could be an option, but it doesn’t sound like one for the masses, though BSD UNIX hardly is at the best of times.

When someone turns to creating a desktop variant of BSD, FreeBSD seems to be a starting point for so much of the time. Even Debian, itself the foundation of so many Linux distributions, bases its own BSD variant on FreeBSD and Gentoo apparently has been looking at doing something similar. FreeBSD does give away a bias towards servers in that the default installation does not include a desktop environment. However, if you do the work, you can get one like GNOME 2 or XFCE on there and the process does remind me of the thinking behind Arch Linux. Until recently, I had FreeBSD 10 installed in a VirtualBox virtual machine until a software update broke it and that does sit well with the BSD culture of stability. Of course, it could be another sign of a focus on server computing too. Nevertheless, it ran well until then and fared no worse than the aforementioned Arch Linux, though it probably should have done better.
Apparently, this is FreeBSD with a choice of MATE (a fork of GNOME 2 for those not fancying the idea of using GNOME 3 and its GNOME Shell), XFCE, LXDE or OpenBox desktop environments. A recent look demonstrated that the desktop environments are turned out very nicely too. All in all, it looks like an interesting counterpart to what you would find with a Linux distro.
Given the troubled state of the online world because of cybercrime and cyberwarfare, it hardly comes as a surprise that computer security has a higher profile than it ever has. It then is hardly surprising that someone decided to create a more secure spin of FreeBSD. For added context, here is what the project had to say about its goals:
HardenedBSD aims to implement innovative exploit mitigation and security solutions for the FreeBSD community. Security is like an onion--it’s made up of layers. To be successful, attackers must peel back each layer. HardenedBSD takes a holistic approach to security by hardening the system and implementing exploit mitigation technologies. We will work with FreeBSD and any other FreeBSD-based project to include our innovations. Our primary goal is to provide a clean-room reimplementation of the publicly documented parts of the grsecurity patchset for Linux.
According to the website, this is a derivative of NetBSD developed with desktop users in mind. At first, it had a feel that would have been more widely available with UNIX and Linux systems in the middle of the 1990’s. Since then, XFCE was chosen as a desktop environment and that has modernised the feel.
Since I last had a look, the focus of this project has become portability. What they mean by portability is have versions of NetBSD that run on all sorts of hardware and I even thought I saw a mention of Sony PlayStation (PS2) if my eyes did not deceive me and ARM-based systems also appeared, hardly a surprise with the rise of tablet computing. Other more conventional computing platforms are served too, but the others make NetBSD stand out from the others more than I once thought it did.
To some, portability is about running software under different hardware architectures. That is not what is meant here since we are talking about the ability to run an installation off a USB drive plugged in to any computer, more likely with Intel and AMD processors. The underlying basis is FreeBSD with OpenBox being the chosen desktop environment, assuring a friendly user interface as well.

With a strap line like “Only two remote holes in the default install, in a heck of a long time!”, you’d have to suspect that security and stability are the key attributes of this operating system. The security aspect certainly crops up a lot so I think that a spot of exploration is in order, especially when various system types (x86 and SPARC are just two of them) are supported anyway. The ongoing furore about intelligence service monitoring and increasing numbers of attacks on different systems over the web do make the whole subject more relevant now than it ever was and it never was irrelevant.
When m0n0wall was discontinued in 2015, OPNsense was forked from pfSense, a move that has left tension between the two projects. The newcomer gave the following reasons for its actions: code quality, regular releases, security issues related to the web UI being run as root, source code for the pfSense build tools is no longer publicly available, concern regarding transparency, new ownership of the pfSense brand, using the brand name to fence off the competition and several licence changes for no apparent reason. These have been contested by the pfSense while OPNsense now uses HardenedBSD as its basis and has stuck with a frequent release model.
This was started in 2004 as a fork of the now defunct m0n0wall with the first public release coming in 2006. It is based on FreeBSD and can be installed on physical or virtual appliances for added network security. It seems to add a BSD installation for a firewall and other security functions, but there clearly is a place for this in the enterprise market by all accounts.
Network-assisted Storage (NAS) has blossomed in recent years for home users and anyone with a DIY mindset might be tempted to go and build things themselves using PC parts and it is for those that this FreeBSD-based distro would be an asset. When I went looking at the possibility, the inability to boot the installation disk that I was using put paid to the attempt. Then, I was left wondering if my use of AMD’s CPU’s was part of the problem, though I since have realised that building a low-power system might be a better option than reusing a full PC. There has been an incursion into the world of NAS drives in the form of a 3 GB Western Digital My Book Live, so any return to DIY ways could be a better informed.
Like TrueNAS, this another BSD for use when making an old PC into a NAS file server. In fact, this came into being when part of the FreeNAS community took exception to the direction in which iXsystems were starting to take it after 2011. It also is based on FreeBSD and has a different web interface. That makes it an alternative if TrueNAS does not do the deed for you.
Solaris
One of the casualties of Oracle’s takeover of Sun Microsystems was the community-based OpenSolaris project. The more proprietary Solaris 11 Express became Oracle’s answer to the need that OpenSolaris fulfilled back then. Since, Solaris 10 & 11 became available without charge with support contracts becoming the revenue earner.
The demise of OpenSolaris saw a major new project emerge. Its basis is Illumos, itself a fork of the now defunct OpenSolaris, and a recent look revealed that it is maturing rather nicely. MATE is the chosen desktop environment so it should not be that unfamiliar to those coming from the Linux world. Initially, there is not so much software installed, but Firefox does get included and there is a graphical package manager, so there is little point in complaining.
The enterprise focus of this offering is plain on the website since virtualisation and the storage platform get a strong showing. Discussion of desktop environments and such like are conspicuous by their absence. Seemingly, this is infrastructural software above all else and there are support contracts available too.
The website for this Illumos distro has a retro, so it is easy to believe that the operating system could be similar. Since MATE, XFCE and Enlightenment are the available desktop environments, anyone coming from Linux should be thrown off very much once they figure out how to get things started.
With a moniker like “Converged Container and Virtual Machine Hypervisor”, this clearly is not a desktop computing offering. There is more than a hint of cloud computing about it and that hardly is a surprise given the age in which we work.